Radiation therapy is the use of high energy ionizing rays or particles to treat cancer. Localized radiation therapy may be given prior to surgery in order to reduce the size of the tumor so that the removal is feasible. After surgery, radiation therapy is used to treat the remaining cancer cells which may be beyond the surgically removed margins. Chemotherapy is sometimes given in combination to enhance the effects of radiation therapy.
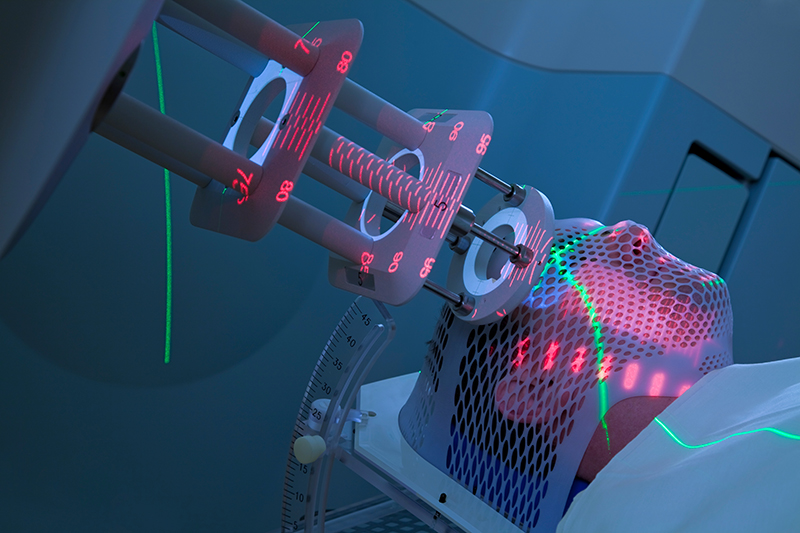
External Beam Therapy : Radiation administered from an external source. Different machines will administer radiation differently depending on the type and extent of the tumor.
Internal (Brachy) Therapy : Radiation or radioactive material is placed within the body, around or in the tumor to destroy the abnormal cells.
Systemic Radiation : Radioactive drugs are administered either through the mouth or through veins in order to treat certain cancers by travelling through the body.
Total Body Irradiation : Uniform dose of radiation therapy administered for the entire body.
Half Body Irradiation : used mostly in case of bone metastasis, upper body or lower body is administered radiation therapy
Hyperthermia : hyperthermia or heat has shown to enhance the effects of radiation therapy as it will cause permanent the radiation-induced chromosomal damage within the cell, thus causing cell death.
Intraoperative Radiation Therapy : upon direct visualization of cancer during surgery, large doses of electron irradiation is used over the tumor to control local reoccurrence
Radiosensitizer : chemical radiosensitizing compounds are used to increase the lethal effects of radiation therapy
Stereotactic External Beam Irradiation : usually used in cranial (brain) surgery. It is also known as the gamma knife where a 3D distribution of the treatment beam is targeted to the tumor.
Skin : skin reactions begin anywhere from 2 weeks into therapy onwards. The reactions may cause reddening, increased sensitivity, dryness, itchiness, flaking and tanning. Post-treatment, the skin reactions will heal in a few weeks, however, skin tanning may take longer.
Fatigue : this is a subjective feeling of tiredness due to tumor breakdown
Anorexia : Loss of appetite
Bone Marrow Suppression : As bone marrow cells are fast multiplying, radiation therapy suppresses the cell reproduction resulting in suppression.
Fertility : it is important that during therapy, women do not get pregnant as radiation can harm the growing baby. It is advised that men do not get women pregnant while undergoing therapy.
Most of the side effects of radiation therapy reverse after therapy is over.